Android and System Level Audio.pptx
Investigation Topics
Things that we need to investigate in order to make the evaluation of which approaches are feasible.
- Raw streams from Android.
- Can we get the raw streams from any source, app, system, etc sent outside of the system without unnecessary preprocessing (see definition of Raw Stream below).
- How is this done?
- Are there limitations? For example, if apps themselves take decision on type, priority, effects, and even volume, then this is not a pure raw stream
- What Raw Stream Metadata (definition below) can be extracted and delivered together with the stream to an outside system.
- Input streams to Android (external sources need to be brought into the Android head unit, if all mixing is done inside Android).
- How is this done?
- Are there limitations on the number of streams?
- Can we bring the required metadata in (or at least associate "hard coded" metadata with the identity of a particular incoming stream. For example we know this one is a prioritized type of stream)
- Any particular support in Android for networked audio? Audio output device?
- Anything to consider about compressed audio / codecs? Support for hardware implementations?
- → Not in AOSP. The connection to hardware accelerators is expected to be implemented by vendor.
Investigation Answers
- Raw streams:
- Streams have properties. It seems any of these encodings might be used in the HAL interface: https://source.android.com/devices/audio/data_formats
- ...but not all compressions might be supported in a particular platform?
- Bartosz to continue here
- What are referred to as metadata match the Android term "attributes", the two main attributes are :
- Usage : (Communication, Alarm, Notification,...) the list is relatively long
- Content type : (Unknown, Movie, Music, Sonification, Speech) and this one is important for post processing configuration
- Streams have properties. It seems any of these encodings might be used in the HAL interface: https://source.android.com/devices/audio/data_formats
- Input streams to Android
- ... todo...
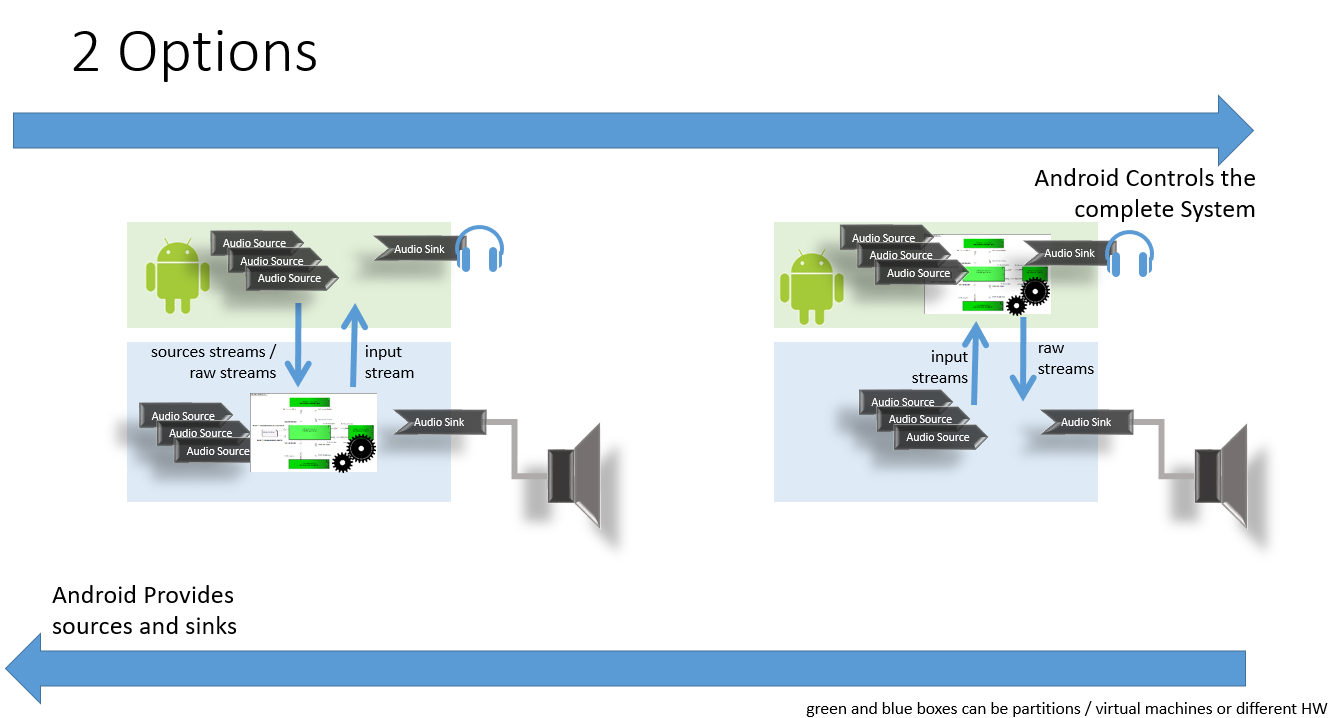
Analysis of both approaches
| Function | Android Provides sources and sinks | Android Controls the complete system |
|---|---|---|
| How to get Raw Streams | applicable (individual streams or / streams per type ?) | applicable (difficulty ?) (individual streams not required / streams per type required ?) |
| Common HAL | ||
| Mixing | then getting raw streams are required |
Possible partitioning over a hybrid approach
| Function | inside Android | outside Android |
|---|---|---|
Definitions
Raw Stream:
- = The audio stream as coming from a source (PCM format mostly, or other encoding such as Dolby for multi-channel, in that case indicate this).
- There shall be none or minimal application of Gain/Volume (stream should be at nominal / maximum volume), Effects (no effects applied), or Mixing (one stream at a time).
- We can however consider 2-ch stereo, or multi-channel, as a single stream as long as it is transferred so that it can be trivially separated for treating the channels separately in the outside system.
Raw stream metadata:
- = Information about the stream.
- Where it is coming from (an app? the HMI? the system?).
- What type of audio is it (Audio track of a video playback? Music? Navigation prompt? Urgent and safety-critical warning message? HMI feedback because you pressed a button?).
- Metadata is used in an external mixing and effects system to take the decision about how to mix, how to apply volume and effects, and especially for priority of one sound over another.
Proof Of Concept - Getting Raw Streams
(screenshot from the attachment below - Piotr Krawczyk - Tieto Evry)